Advanced Launch Configurations
Beyond the Quick Start and Configuring MoveIt Pro guides, there are many advanced ways to install and run MoveIt Pro, discussed here.
Run Drivers Separately
You can disable bringing up the drivers with MoveIt Pro by using the command moveit_pro run --no-drivers
If you are required to bring up just the drivers, you can use the moveit_pro run --only-drivers command.
This will be useful when bringing up MoveIt Pro between two computers where one computer can be used to run the drivers and the rest can launch the other components of MoveIt Pro.
Build and Test Your Workspace
If you mounted a user workspace from your host into MoveIt Pro, the packages in that workspace will be mounted to the ${HOME}/user_ws folder inside the relevant containers.
This gives you access to a few more useful Docker services:
Build and run tests in your workspace by using the commands moveit_pro build user_workspace and moveit_pro test, respectively.
Introspecting in MoveIt Pro
The web app displays key information (such as Objective successes or failures). However, during your development you may need to analyze results in more detail.
Using the ROS 2 Command-Line interface
From the current MoveIt Pro install folder, you can open an interactive Bash session with the MoveIt Pro Agent Docker container:
moveit_pro shell
Once you are inside the container, ensure to source the MoveIt Pro workspace. Then, you can use the ROS 2 command-line interface (CLI) to introspect nodes, topics, and more.
source /opt/overlay_ws/install/setup.bash
ros2 node list
ros2 topic echo /joint_states
If you mounted a user workspace from your host, you should instead source that workspace using:
source ~/user_ws/install/setup.bash
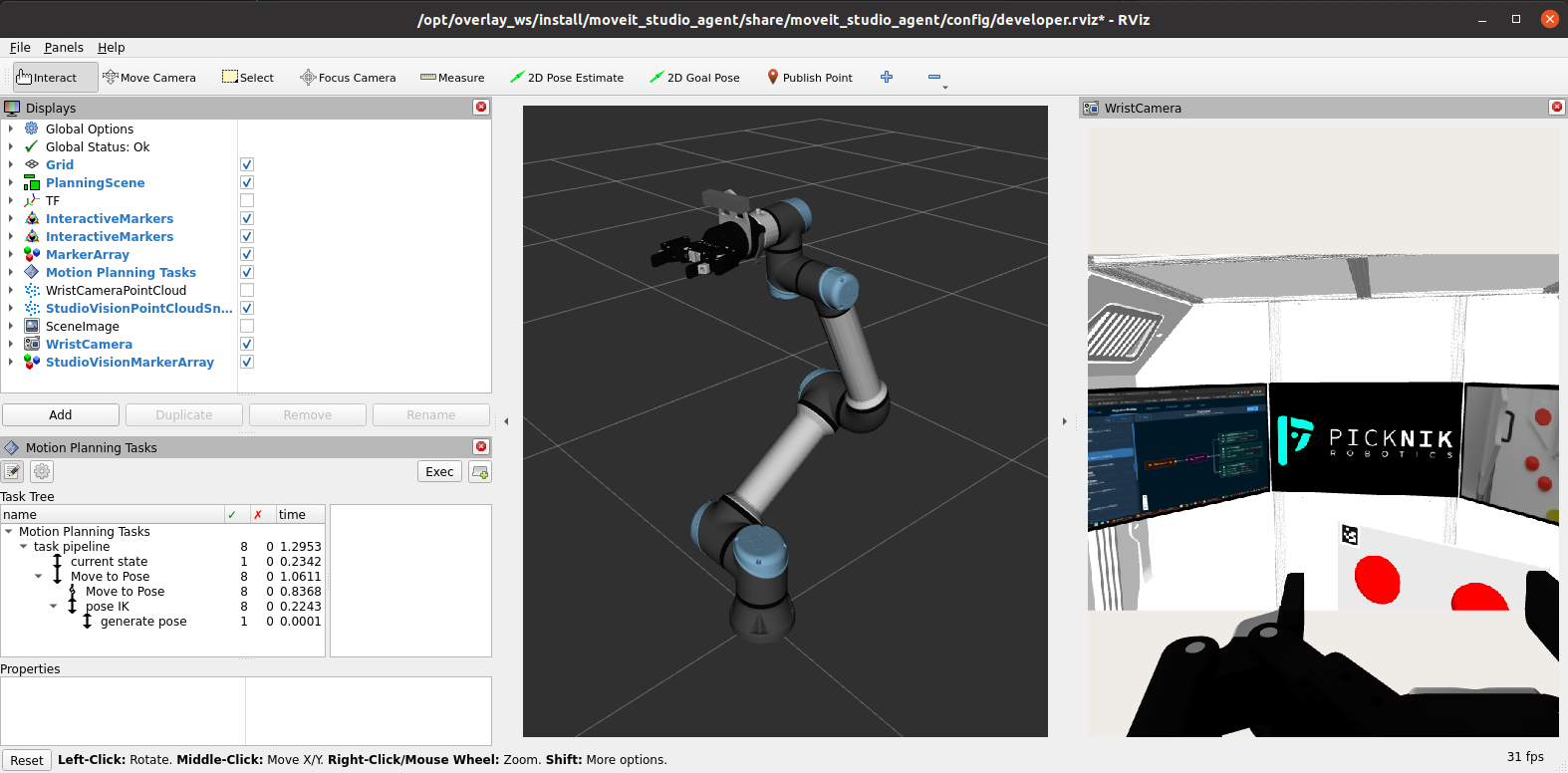
Visual Debugging with RViz
MoveIt Pro provides a default RViz configuration for visual debugging. For example, this easily lets you analyze camera feeds, the TF tree, motion planning results, and more.
moveit_pro rviz